The <progress> HTML Tag
Braydon Coyer / January 05, 2021
2 minute read
•
1497 views
Welcome to the first article in the Uncommon HTML Tags series! With each article in this series, I will introduce a widely unknown HTML tag, discuss compatibility across browsers and cover some real-world use cases with the element.
My hope is that each article broadens your understanding of HTML and helps you discover new tags.
The <progress></progress> tag will create a progress bar and allow you to visualize the completion of a task. This could be handy for showing the progress completion of a multi-page feedback survey, for example!
Let's take a look at how it's used!
1<label for="progress">Article Progress:</label>2
3<progress id="progress" max="100" value="50">50%</progress>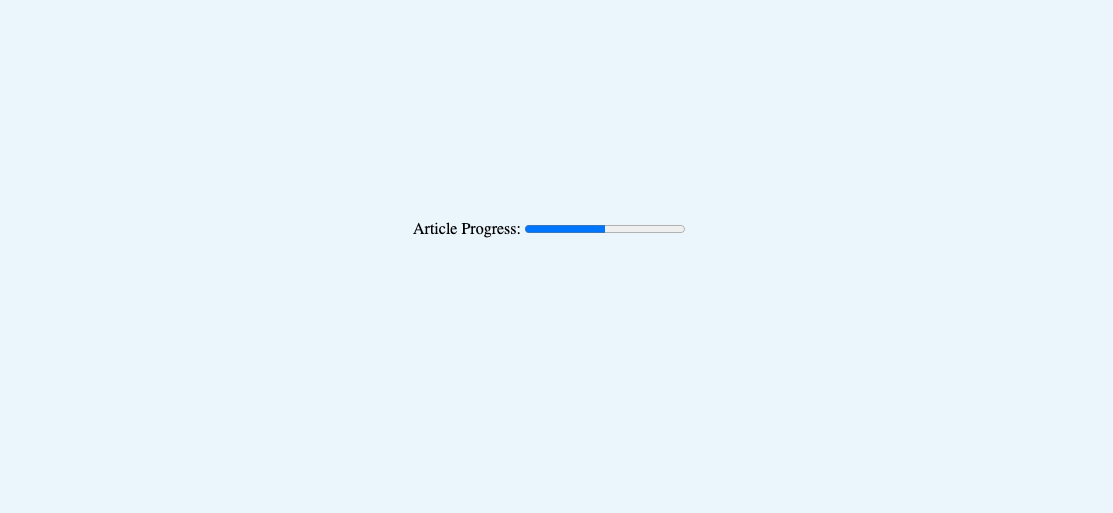
As seen in the example above, there are two attributes you can use on the element.
max- this attribute, if used, is a floating point number and must have a value greater than0.value- this optional attribute is used to determine the completion of a task and must be a floating point number between0and the number set in themaxattribute. If thevalueattribute is omitted, the progress bar is set to an indeterminate state.
Here is an example of an indeterminate progress bar:
1<label for="progress">Article Progress:</label>2
3<progress id="progress" max="100"></progress>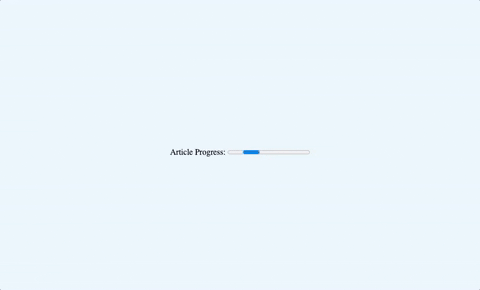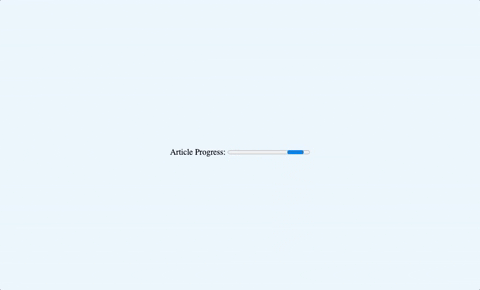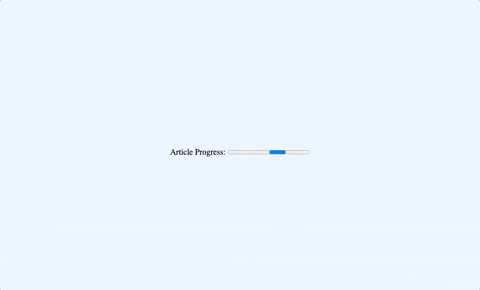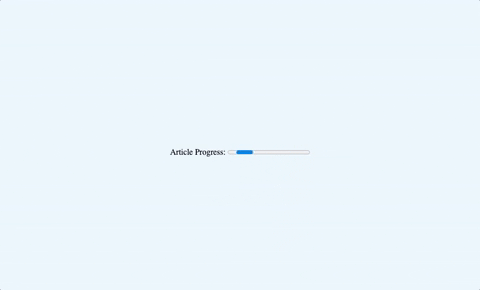
If you want to play around with the tag, feel free to fork the pen below!
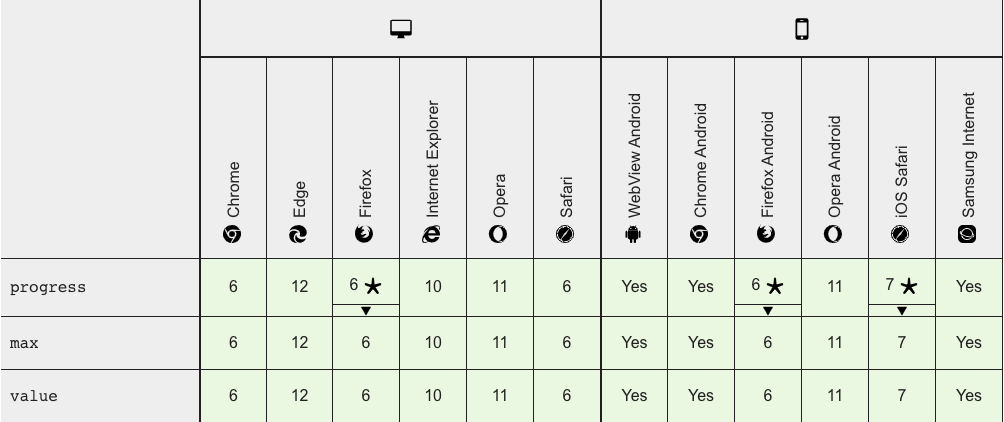
The <progress></progress> tag is part of the HTML5 Standard and is supported on all major web browsers. No need to worry about compatibility issues!
Have you ever used the <progress></progress> tag in a project? Hit me up on Twitter and let me know!
Thanks for reading! If you liked this article and want more content like this, read some of my other articles and make sure to follow me on Twitter!
Articles delivered to your inbox!
A periodic update about my life, recent blog posts, how-tos, and discoveries.
As a thank you, I'll also send you a FREE CSS tutorial!
No spam - unsubscribe at any time!